Introduction to Artificial Superintelligence (ASI)
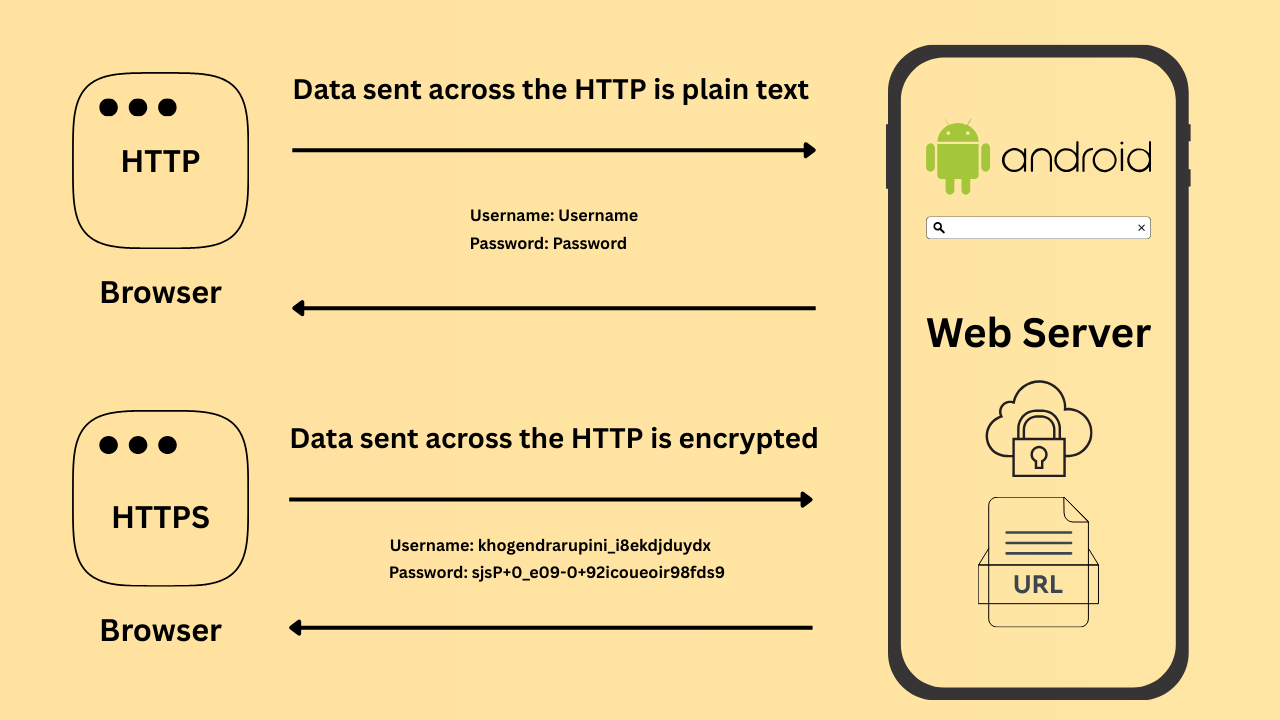
When you browse the internet, you’ve likely noticed that website addresses often begin with either http:// or https:// . These prefixes indicate the protocol used to transfer data between your web browser and the website you are visiting. While both HTTP and HTTPS serve as communication protocols, they differ in significant ways—most importantly, in terms of security.
This article explains what HTTP and HTTPS are, highlights their key features, and discusses why HTTPS has become the preferred standard over HTTP.
HTTP stands for HyperText Transfer Protocol . It was invented by Tim Berners-Lee and serves as the foundation for communication on the World Wide Web.
HyperText refers to text that is specially formatted using a standard coding language called HyperText Markup Language (HTML) . HTTP defines a set of rules that allows web browsers and web servers to communicate , enabling the transfer of data such as text, images, and multimedia files between computers.
Each time a user opens a web browser, they are indirectly relying on HTTP to request and receive content. As an application-level protocol , HTTP is designed for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems, making it a core element of the modern internet.
Characteristics of HTTP
- Protocol: HTTP is an IP-based communication protocol used to deliver data between a server and a client.
- Content Exchange: Any type of content can be transmitted as long as both the server and client support it.
- Request–Response Model: It operates as a request and response protocol based on client and server requirements.
HTTP Request
An HTTP request is a message sent by a client typically a web browser to a server in order to access specific resources. This request includes several components, such as the request method (e.g., GET, POST, and others) , headers , and in some cases, a body that carries data . Through this process, the client specifies what it needs from the server and how the request should be handled.
HTTP Response
An HTTP response is the message a server sends back to a client after receiving an HTTP request . It typically includes three main components: a status code , which indicates the outcome of the request; headers , which provide metadata about the response; and a body , which contains the requested resource or an error message if the request could not be fulfilled.
How Does the HTTP Protocol Work?
The HTTP protocol operates on a request–response model . When a client needs information, it sends an HTTP request to the server. The server then processes the request and replies with an HTTP response , which may include the requested data or an error message. This exchange occurs over the internet, typically using port 80 by default . For identification purposes, this protocol is generally referred to as HTTP .
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. It is essentially the standard HTTP protocol combined with SSL/TLS encryption, which enables secure communication and authentication between a client and a web server. HTTPS provides a higher level of security than HTTP because it uses SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificates to verify and protect the connection. When a website uses only HTTP in its URL, the connection is not secure, whereas HTTPS ensures that data exchanged between the browser and server is encrypted and safeguarded.
Characteristics of HTTPS
- Encryption: HTTPS secures all message content, including HTTP headers and request/response data.
- Authentication: It requires a trusted third party to sign server-side digital certificates for verification.
- Usage: HTTPS is now used far more widely than non-secure HTTP, primarily to ensure website authenticity, protect user accounts, and safeguard client communications across all types of websites.
In summary, both HTTP and HTTPS are protocols that enable the exchange of information between a web server and a web browser. However, the key distinction lies in security: HTTPS provides a much higher level of protection compared to HTTP, making it the preferred choice for modern websites.
How Does the HTTPS Protocol Work?
HTTPS functions similarly to HTTP, but with an added layer of security. It establishes a secure connection between the client and server using SSL/TLS, which encrypts all communications between them. When a client requests a resource over HTTPS, the client and server negotiate encryption keys that will be used for that specific session. This process ensures that the transmitted data is encrypted, protected, and cannot be intercepted or tampered with during exchange.
Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS
| Feature | HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) | HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The foundational protocol for transmitting data across the World Wide Web. Data is sent in plain text. | An extension of HTTP. It uses encryption (SSL/TLS) to secure the communication between a client and a server. |
| Protocol | Operates over TCP/IP. | Operates over TCP/IP but uses an additional SSL/TLS protocol to encrypt the HTTP communication. |
| Port | Uses Port 80 by default. | Uses Port 443 by default. |
| Data Encryption | No encryption. All data is transmitted in plain text. | Fully encrypted. Uses SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt all data exchanged between the client and server. |
| Security | Insecure. Vulnerable to eavesdropping, man-in-the-middle attacks, and data tampering. | Secure. Protects against eavesdropping, tampering, and message forgery through encryption and authentication. |
| Data Integrity | No data integrity. There is no way to verify if the data was altered during transmission. | Ensures data integrity. The encrypted data cannot be altered during transit without being detected. |
| SSL Certificate | Not required. | Required. A valid SSL/TLS certificate issued by a Certificate Authority (CA) must be installed on the web server. |
| Validation | No validation of the server's identity is performed. | Validates that the user is communicating with the intended, legitimate website and not an imposter. |
| SEO (Search Ranking) | Google and other search engines penalize HTTP sites, ranking them lower. | Google rewards HTTPS sites with a ranking boost, making it a standard best practice. |
| Browser Display | Modern browsers (Chrome, Firefox, etc.) mark HTTP sites as "Not Secure" in the address bar. | Displayed with a lock icon 🔒 in the address bar, indicating a secure connection. |
| Speed & Performance | Slightly faster because there is no encryption/decryption overhead. | Historically slower due to encryption overhead, but with modern protocols (TLS 1.3) and hardware, the difference is now negligible. |
| Use Cases | Suitable for non-sensitive, public information websites (e.g., basic blogs, news sites) where security is not a concern. | Essential for handling sensitive information such as logins, payment details, personal data, and any website prioritizing user trust. |
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is the protocol used to transfer hypertext across the web. Its simplicity has made it one of the most widely adopted protocols for data exchange online. However, data transmitted through HTTP is not inherently secure. To address this limitation, cryptographic protocols such as SSL (Secure Socket Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are applied to HTTP, creating HTTPS. In short, HTTPS = HTTP + SSL/TLS encryption, which ensures confidentiality, integrity, and secure communication.
Conclusion
HTTP and HTTPS are both protocols used to transfer data across the web. The key difference lies in security: HTTPS is encrypted and authenticated, making it far more secure than HTTP. While HTTP is generally sufficient for delivering non-sensitive content, HTTPS is essential for protecting user information and securing online transactions. With the advancement of modern technologies, HTTPS has increasingly become the standard for safe and reliable web browsing.
Edit Profile
Help improve @KR
Was this page helpful to you?
Contact Khogendra Rupini
Are you looking for an experienced developer to bring your website to life, tackle technical challenges, fix bugs, or enhance functionality? Look no further.
I specialize in building professional, high-performing, and user-friendly websites designed to meet your unique needs. Whether it’s creating custom JavaScript components, solving complex JS problems, or designing responsive layouts that look stunning on both small screens and desktops, I can collaborate with you.
Create something exceptional with us. Contact us today
Open for Collaboration
If you're looking to collaborate, I’m available for a variety of professional services, including -
- Website Design & Development
- Advertisement & Promotion Setup
- Hosting Configuration & Deployment
- Front-end & Back-end Code Implementation
- Code Testing & Optimization
- Cybersecurity Solutions & Threat Prevention
- Website Scanning & Malware Removal
- Hacked Website Recovery
- PHP & MySQL Development
- Python Programming
- Web Content Writing
- Protection Against Hacking Attempts